Sebaceous Cyst Surgery
Sebaceous Cyst Surgery
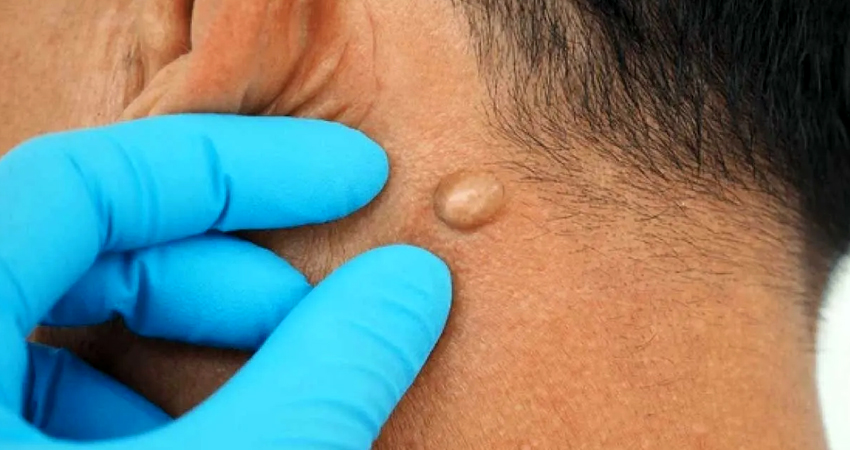
A sebaceous cyst (also called an epidermoid cyst or epidermal inclusion cyst) is a common, benign, slow-growing lump that develops under the skin.
Origin: Arises from blocked sebaceous glands or hair follicles. It contains keratin and lipid-rich debris, not true sebum.
Common Sites: Scalp, face, neck, back, trunk, scrotum.
Appearance:
- Smooth, round, firm, mobile lump under the skin.
- Size varies (few mm to several cm).
- Sometimes has a visible punctum (tiny black opening).
Symptoms:
- Usually painless.
- May become painful, red, and swollen if infected.
- Can discharge foul-smelling, cheesy material if ruptured.
Diagnosis:
- Clinical examination is usually sufficient.
- Ultrasound can confirm cystic nature if needed.
- Histopathology after excision to rule out rare malignancy (sebaceous carcinoma, SCC).
Management:
1. Asymptomatic, small cysts → Observation only.
2. Symptomatic / cosmetic concern / recurrent infection →
- Complete surgical excision with wall intact (to prevent recurrence).
- Incision & drainage only if infected, followed by delayed excision after inflammation subsides.
3. Antibiotics if secondarily infected.
Complications:
- Infection → abscess formation.
- Rupture → inflammation, scarring.
- Rare malignant transformation (extremely uncommon)
-

Cashless Facility Available
-

All mediclaim/Health Insurance Accepted
-

EMI Payment Option Available
-
Free Guidance to choose right Health Insurance
-
Home Visit Available
